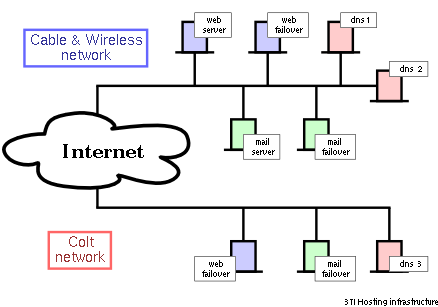
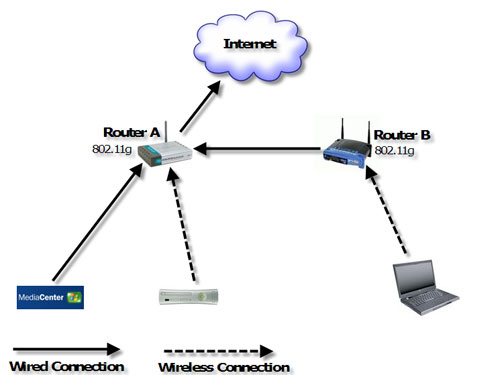
The internet in simple terms is a network of the interlinked
computer networking worldwide, which is accessible to the general public. These
interconnected computers work by transmitting data through a special type of
packet switching which is known as the IP or the internet protocol.
Internet is such a huge network of several different
interlinked networks relating to the business, government, academic, and even
smaller domestic networks, therefore internet is known as the network of all
the other networks. These networks enable the internet to be used for various
important functions which include the several means of communications like the
file transfer, the online chat and even the sharing of the documents and web
sites on the WWW, or the World Wide Web.
The use of IP in the Internet is the integral part of the
network, as they provide the services of the internet, through different layers
organization through the IP data packets. There are other protocols that are
the sub-classes of the IP itself, like the TCP, and the HTTP.
Internet infrastructures :
Internet Protocol (IP) :
- The Internet Protocol (IP) is the principal communications
protocol used for relaying datagrams (also known as network packets) across an
internetwork using the Internet Protocol Suite. Responsible for routing packets
across network boundaries, it is the primary protocol that establishes the
Internet.
IP is the primary protocol in the Internet Layer of the
Internet Protocol Suite and has the task of delivering datagrams from the
source host to the destination host solely based on the addresses. For this
purpose, IP defines datagram structures that encapsulate the data to be delivered.
It also defines addressing methods that are used to label the datagram source
and destination.
Historically, IP was the connectionless datagram service in
the original Transmission Control Program introduced by Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn
in 1974, the other being the connection-oriented Transmission Control Protocol
(TCP). The Internet Protocol Suite is therefore often referred to as TCP/IP.
Function of IP :
- The Internet Protocol is responsible for addressing hosts
and routing datagrams (packets) from a source host to the destination host
across one or more IP networks. For this purpose the Internet Protocol defines
an addressing system that has two functions: identifying hosts and providing a
logical location service. This is accomplished by defining standard datagrams
and a standard addressing system.
Each datagram has two components, a header and a payload.
The IP header is tagged with the source IP address, destination IP address, and
other meta-data needed to route and deliver the datagram. The payload is the
data to be transported. This process of nesting data payloads in a packet with
a header is called encapsulation.
Perhaps the most complex aspects of IP are IP addressing and
routing. Addressing refers to how end hosts are assigned IP addresses and how
subnetworks of IP host addresses are divided and grouped. IP routing is
performed by all hosts, but most importantly by routers, which typically use
either interior gateway protocols (IGPs) or external gateway protocols (EGPs)
to decide how to move datagrams among networks.
IP routing is also common in local networks. For example,
Ethernet switches sold today support IP multicast. These switches use IP addresses and Internet
Group Management Protocol for control of the multicast routing but use MAC
addresses for the actual routing.